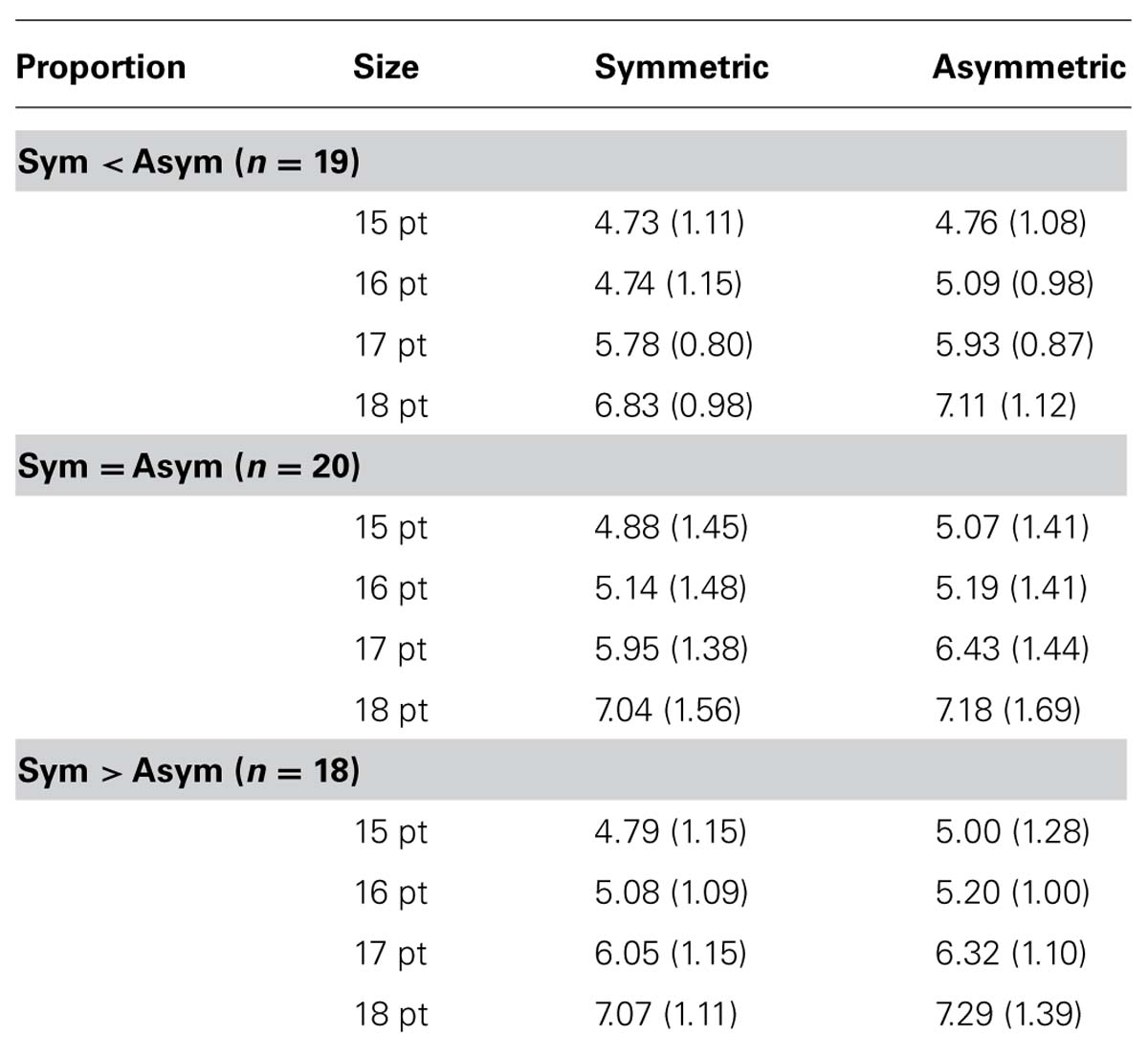
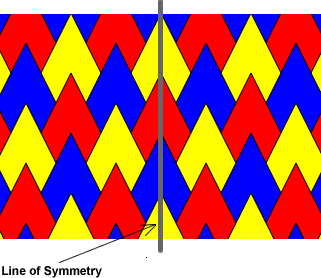
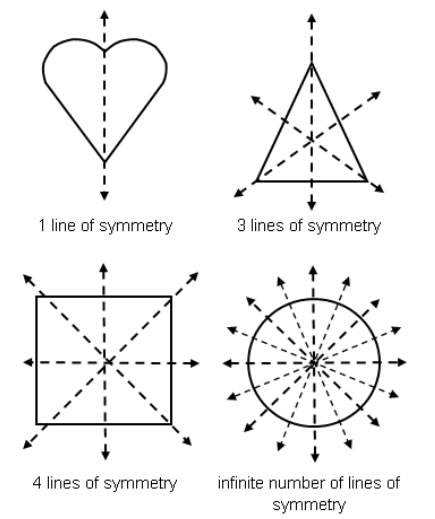
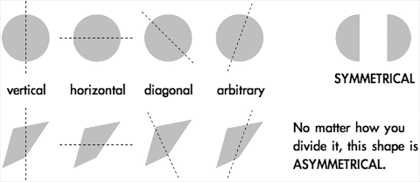
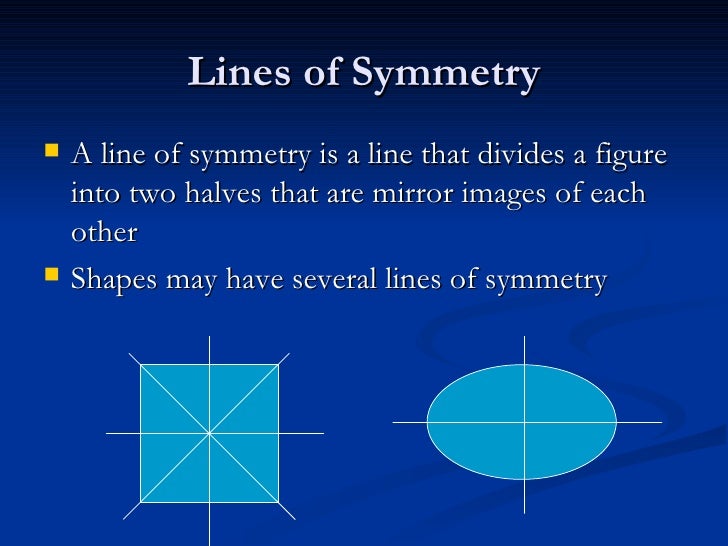
What Does Symmetry Mean. What does symmetry mean in math? Symmetry (physics), a physical or mathematical feature of the system (observed or intrinsic) that is "preserved" under some change.

But if we take the side view of our face and fold it, we do not get symmetrical shapes as one part is.
A global symmetry is one where the symmetry parameter is simply a constant — and hence the transformation is applied uniformly across the entire system.
However, all symmetries of a differential equation do not necessarily arise from symmetries of the action when there is a variational principle. They can be analyzed using local symmetry.• This idea is attractive because it would mean a nice symmetry between the expanding and contracting phases.• Meaning of symmetry. Symmetry is a type of invariance: the property that something does Geometrically speaking, the graph face of an even function is symmetric with respect to the y-axis, meaning that its graph remains unchanged after.